- Home
- Products
- Video
- Blog
- Projects
- Quality Control
- About ALM
- News
- Support
- Contact Us
Views: 16 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2023-02-09 Origin: Site

In profiled rail linear guides using balls or rollers,the geometry and arrangement of the bearing raceways play an important role in the bearing's load capacity,friction,stiffness and ability to withstand mounting errors.However,another aspect of the bearing design also plays a role in its load capacity and stiffness-the contact angle.
●45 degree contact angles for equal load capacity
Linear guides using gothic arch geometry(including miniature profile guides and most roller bearing guides)have four points of contact between the ball and the raceway,resulting in a contact angle of 45 degrees.
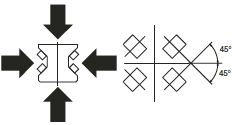
Bearings that use a 45 degree contact angle have equal load capacities in all four primary directions.
The benefit of the 45 degree angle is that it provides equal load capacity for the bearing in all four major directions-radial(down and up)and lateral(side)loads.This means the guide can be used in any direction without reducing load capacity.
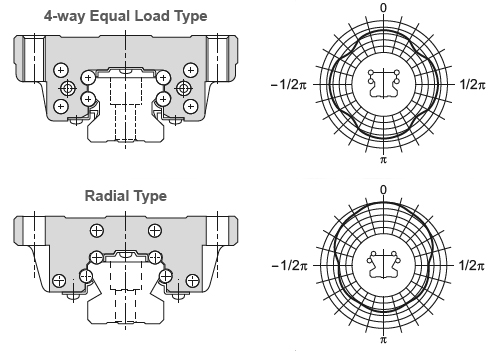
Top:When the contact angle is 45 degrees for all rows of balls,the load capacity is the same in all four directions.
Bottom:When the contact angle is larger for the top rows of balls,the load capacity is higher in the radial direction but lower in the reverse radial and lateral directions.
●Higher contact angles for better radial load capacity
On the other hand,linear guides using circular arc or offset gothic arch geometries can be designed with different contact angles to produce a higher load rating in one direction,despite sacrificing load capacity in the other direction.
For example,an arc design uses a 90-degree contact angle on the top row of balls and a smaller angle of 30 degrees on the bottom row of balls.This allows the bearing to have extremely high load capacity under radial(downward)loads,which is the primary load direction in many applications,because the load is transferred from the top row of balls directly down into the raceway.It also gives the bearing very high rigidity(low deflection)when radial loads are applied.The trade-off for higher load capacity and rigidity in the radial direction is lower load capacity and rigidity in the reverse radial and lateral directions.
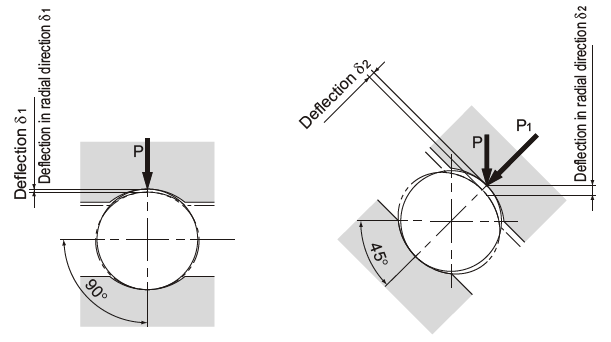
The closer the contact angle is to 90 degrees,the lower the deflection in the radial direction.
Another design is based on an offset Gothic arch geometry using a 50 degree contact angle for all four rows of balls.This provides a higher load capacity in the radial and reverse radial directions,but a lower load capacity in the lateral direction.
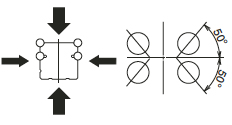
The bearing uses a 50 degree contact angle for all four rows of balls,giving it a high load capacity in the radial and reverse radial directions,but a low load capacity in the transverse direction.
Click to select ALM high quality linear motion components for your application:
www.autolinearmotion.com/products.html