- Home
- Products
- Video
- Blog
- Projects
- Quality Control
- About ALM
- News
- Support
- Contact Us
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
1205
ALM
8483401000
Ball screws or lead screws,how to choose?
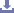
ALM manufactures both lead and ball screws so consider these comments as unbiased.In fairly basic terms, lead screws are used when linear speeds are slow (slower than 50 mm/sec), loads are light (i.e. the automated machine axis is on the small side) and cost is the primary concern.
Ball screws will always be more expensive – why? That's easy – there are more parts.
A lead screw is merely a threaded shaft and simple nut. The precision of such a device is based on the grind accuracy for the shaft and the resultant play when the nut is installed. And there will always be play if the lead screw only has a single nut – otherwise there must be an interence fit which means very high friction. ALM lead screws can be provided with play down to several microns but to completely eliminate play in a lead screw requires two nuts, with a spring in between.
Why the speed limitation? That's due to the friction which limits the efficiency to at best about 50%. Compare that to a ball screw, which achieves efficiencies approaching and exceeding 90%. But this high efficiency also means that ball screws can be back driven – which may or may not be desirable. Lead screws typically cannot be back driven.
Ball screws are more susceptible than lead screws to contamination.Lead screws require less lubrication – some operate quite well without any oil or grease. Shaft manufacturing is comparable on both lead screws and ball screws – the thread can be rolled, whirled or ground.
As for material, ball screw and lead screw shafts are typically manufactured from either tool steel or stainless steel. Lead screw nuts are available in plastic material (hence the low cost) or bronze or similar softer materials with low coefficient of friction, while ball screw nuts, and the balls inside, require the same hardness as the shaft (generally at least HRC 58).
Finally, another good thing about lead screws – you can spin the nut off the shaft quite easily – and then re-install. It’s a lot harder with ball screws – and without a proper tool, spinning the nut off the shaft results in a lot of balls on the floor and a very unhappy customer!
ALM can not only produce ground ball screws,but also the rolled types.
Rolled ball screws range:Diameter 4mm to 120mm.
Popular items:0401, 0601, 0602, 0606, 0801, 0802.5, 0805, 0808, 0812,1002, 1202, 1205, 1210
Accuracy can be C3 C5 C7
Lead time:3~10 days
Ground ball screws range:Diameter 3mm to 120mm.
Accuracy can be C1 C3 C5 C7
Lead time:10~30 days
Definition of Mounting Ball Screw Accuracy and Ball Screw Tolerance.
The main items of the mounting accuracy of ball screw are listed in below.
(1) Periphery run-out of the supporting part of the screw shaft to the screw groove.
(2) Concentricity of a mounting portion of the shaft to the adjacent ground portion of the screw shaft.
(3) Perpendicularity of the shoulders to the adjacent ground portion of tha screw shaft.
(4) Perpendicularity of the nut flange to the axis of the screw shaft.
(5) Concentricity of the ball nut diameter to the screw groove.
(6) Parallelism of the mounting surface of a ball nut to the screw groove.
(7) Total run-out of the screw shaft to the axis of the screw shaft.
According to the standard of JIS,we classified our lead accuracy through E, e, e300 and e2π, four main regulations. As figure 1.3.1 ~ 1.3.3 shown in below, all the definition and tolerance are specified.
To test the accumulated travel deviations for grade C7 and C10, the tolerance will be chosen in
random 300mm of useful length and evaluated if it is qualified with the e300 table of 1.3.3.
| Terms | Reference | Definition | Allowable |
Travel Compensation |
T | Travel compensation is the deduction between specified and nominal travel in the useful travel. A slightly smaller value compared with nominal travel is often selected by customer, to compensate for an expected elongation caused by temperature rise or external load. Therefore ” T ” is usually a negative value. Note : if no compensation is needed, specified travel is the same as nominal travel. | |
| Actual Travel | Actual travel is the axial displacement of the nut relative to the screw shaft. | ||
| Mean Travel | Mean travel is the linear best fit line of actual. This could be obtained by the least squares method. This line represents the tendency of actual travel. | ||
Mean Travel Deviation | E | Mean travel deviation is the deduction between mean travel and specified travel within travel length. | Table 1.3.2 |
Travel Variations | e e300 e2π | Travel variations is the coverage of 2 lines drawn parallel to the mean travel. Maximum width of variation within the travel length. Actual width of variation for the length of 300mm taken anywhere within the travel length.Wobble error, actual width of variation for one revolution (2π radian) | Table 1.3.2 Table 1.3.3 Table 1.3.3 |
Cautions About Use of Ball Screws:Ball screw assemblies are delicate components.Therefore,extra care must be taken to prevent the ball track from damages that caused by edged component or tools.
Meanwhile, the steel ball is very easily fall out of the nut or over stroke. Don't disassemble it.
Otherwise,the ball screw will be damaged.
To prevent steel ball fall out of the nut through the disassembly of screw and nut or over stroke, please be careful while operating.
If the steel ball falls out, please contact with ALM Linear Motion for further instruction.Do not attempt to reassemble, which might cause permanent damage to the ball screw.
If disassemble is required, please use a transfer pipe which has minor diameter than the screw
diameter to transfer the nut to prevent falling out of the steel balls.
Email or call us for a quote right now!
sales@autolinearmotion.com
Ball screws or lead screws,how to choose?
ALM manufactures both lead and ball screws so consider these comments as unbiased.In fairly basic terms, lead screws are used when linear speeds are slow (slower than 50 mm/sec), loads are light (i.e. the automated machine axis is on the small side) and cost is the primary concern.
Ball screws will always be more expensive – why? That's easy – there are more parts.
A lead screw is merely a threaded shaft and simple nut. The precision of such a device is based on the grind accuracy for the shaft and the resultant play when the nut is installed. And there will always be play if the lead screw only has a single nut – otherwise there must be an interence fit which means very high friction. ALM lead screws can be provided with play down to several microns but to completely eliminate play in a lead screw requires two nuts, with a spring in between.
Why the speed limitation? That's due to the friction which limits the efficiency to at best about 50%. Compare that to a ball screw, which achieves efficiencies approaching and exceeding 90%. But this high efficiency also means that ball screws can be back driven – which may or may not be desirable. Lead screws typically cannot be back driven.
Ball screws are more susceptible than lead screws to contamination.Lead screws require less lubrication – some operate quite well without any oil or grease. Shaft manufacturing is comparable on both lead screws and ball screws – the thread can be rolled, whirled or ground.
As for material, ball screw and lead screw shafts are typically manufactured from either tool steel or stainless steel. Lead screw nuts are available in plastic material (hence the low cost) or bronze or similar softer materials with low coefficient of friction, while ball screw nuts, and the balls inside, require the same hardness as the shaft (generally at least HRC 58).
Finally, another good thing about lead screws – you can spin the nut off the shaft quite easily – and then re-install. It’s a lot harder with ball screws – and without a proper tool, spinning the nut off the shaft results in a lot of balls on the floor and a very unhappy customer!
ALM can not only produce ground ball screws,but also the rolled types.
Rolled ball screws range:Diameter 4mm to 120mm.
Popular items:0401, 0601, 0602, 0606, 0801, 0802.5, 0805, 0808, 0812,1002, 1202, 1205, 1210
Accuracy can be C3 C5 C7
Lead time:3~10 days
Ground ball screws range:Diameter 3mm to 120mm.
Accuracy can be C1 C3 C5 C7
Lead time:10~30 days
Definition of Mounting Ball Screw Accuracy and Ball Screw Tolerance.
The main items of the mounting accuracy of ball screw are listed in below.
(1) Periphery run-out of the supporting part of the screw shaft to the screw groove.
(2) Concentricity of a mounting portion of the shaft to the adjacent ground portion of the screw shaft.
(3) Perpendicularity of the shoulders to the adjacent ground portion of tha screw shaft.
(4) Perpendicularity of the nut flange to the axis of the screw shaft.
(5) Concentricity of the ball nut diameter to the screw groove.
(6) Parallelism of the mounting surface of a ball nut to the screw groove.
(7) Total run-out of the screw shaft to the axis of the screw shaft.
According to the standard of JIS,we classified our lead accuracy through E, e, e300 and e2π, four main regulations. As figure 1.3.1 ~ 1.3.3 shown in below, all the definition and tolerance are specified.
To test the accumulated travel deviations for grade C7 and C10, the tolerance will be chosen in
random 300mm of useful length and evaluated if it is qualified with the e300 table of 1.3.3.
| Terms | Reference | Definition | Allowable |
Travel Compensation |
T | Travel compensation is the deduction between specified and nominal travel in the useful travel. A slightly smaller value compared with nominal travel is often selected by customer, to compensate for an expected elongation caused by temperature rise or external load. Therefore ” T ” is usually a negative value. Note : if no compensation is needed, specified travel is the same as nominal travel. | |
| Actual Travel | Actual travel is the axial displacement of the nut relative to the screw shaft. | ||
| Mean Travel | Mean travel is the linear best fit line of actual. This could be obtained by the least squares method. This line represents the tendency of actual travel. | ||
Mean Travel Deviation | E | Mean travel deviation is the deduction between mean travel and specified travel within travel length. | Table 1.3.2 |
Travel Variations | e e300 e2π | Travel variations is the coverage of 2 lines drawn parallel to the mean travel. Maximum width of variation within the travel length. Actual width of variation for the length of 300mm taken anywhere within the travel length.Wobble error, actual width of variation for one revolution (2π radian) | Table 1.3.2 Table 1.3.3 Table 1.3.3 |
Cautions About Use of Ball Screws:Ball screw assemblies are delicate components.Therefore,extra care must be taken to prevent the ball track from damages that caused by edged component or tools.
Meanwhile, the steel ball is very easily fall out of the nut or over stroke. Don't disassemble it.
Otherwise,the ball screw will be damaged.
To prevent steel ball fall out of the nut through the disassembly of screw and nut or over stroke, please be careful while operating.
If the steel ball falls out, please contact with ALM Linear Motion for further instruction.Do not attempt to reassemble, which might cause permanent damage to the ball screw.
If disassemble is required, please use a transfer pipe which has minor diameter than the screw
diameter to transfer the nut to prevent falling out of the steel balls.
Email or call us for a quote right now!
sales@autolinearmotion.com